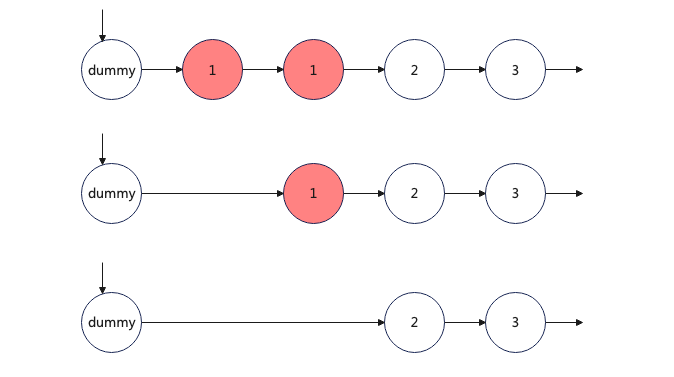
链表
lc.206.反转链表
原题:https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/description/
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var reverseList = function (head) {
let pre = null;
let cur = head;
while (cur) {
let nxt = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = nxt;
}
return pre;
};解释: 需要一个 pre 指针保存 cur 指针上一个节点,同时需要个 next 指针保存 cur.next 的节点, 在这之后 cur 的下一个直线前置节点,实现反转 最后先更新 pre,再更新 cur。 最终 cur 为空,返回 pre 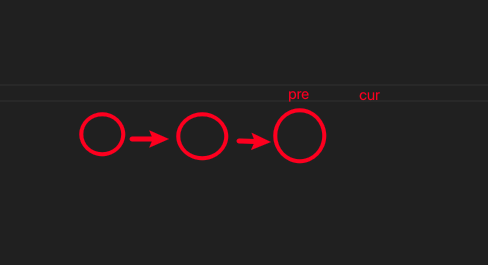
lc.92.反转链表 II
原题:https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list-ii/description/
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @param {number} left
* @param {number} right
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var reverseBetween = function (head, left, right) {
let dummy = new ListNode(); //先保存最初位置
dummy.next = head;
let p0 = dummy;
// 考虑left可能就是head,引入p0
// p0的位置在于初始left的上一个节点
Array(left - 1)
.fill(0)
.forEach(() => {
p0 = p0.next;
});
// 这部分和反转列表一致
let pre = null;
let cur = left;
Array(right - left + 1)
.fill(0)
.forEach(() => {
let nxt = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = nxt;
});
// 重新链接
p0.next.next = cur; // 已有的要先绑
p0.next = pre; // 如果先绑定这个,那po.next.next就变了
return dummy.next; // 一开始保留的开始head,
};解释: 这里要考虑 第一种情况,反转部分,所以要保留 dummy 一开始的指向。 第二种情况,就是 left 就是 head 的时候 细节参考代码注释
lc.25. K 个一组翻转链表
原题:https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-nodes-in-k-group/description/ 细节:每 k 个一组翻转,小于 k 就不反转
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @param {number} k
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var reverseKGroup = function (head, k) {
let dummy = new ListNode();
dummy.next = head;
let p0 = dummy;
// 先记录总个数
let n = 0;
let coutCur = head;
while (coutCur) {
n++;
coutCur = coutCur.next;
}
let pre = null;
let cur = head;
// 多少组
while (n >= k) {
pre = null;
n -= k;
let count = k;
// 每k个为一组翻转
while (count > 0) {
count--;
let nxt = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = nxt;
}
// !!临时变量,这一组结束后,p0要移动到这一组翻转后,结尾的位置,循环开始
let tempP0 = p0.next;
p0.next.next = cur;
p0.next = pre;
p0 = tempP0;
}
return dummy.next;
};解释:与 lc.92 的区别在于,每 k 个为一组进行翻转。 也就是每做完一组,需要重新更新 p0 到这一组翻转后结尾的位置 pre=null
lc.876. 链表的中间结点
原题:https://leetcode.cn/problems/middle-of-the-linked-list/description/
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var middleNode = function (head) {
let slow = head;
let fast = head;
while (fast && fast.next) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
};解释: 原理:slow 走一步,fast 走两步 如图观察,偶数个数 fast 为空;奇数个数 fast.next 为空,当满足其中一个到时候,slow 的位置就是题目所求中间的位置 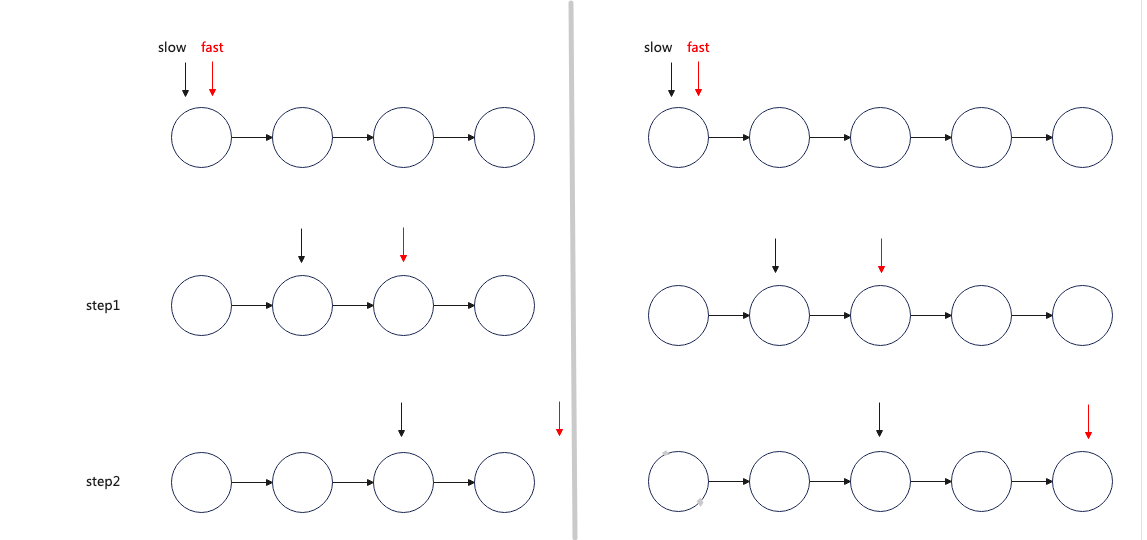
lc. 141.环形链表
原题:https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle/description/
let slow = head;
let fast = head;
while (fast && fast.next) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (fast === slow) {
return true;
}
}
return false;解释:如果有环,快指针一定会套圈慢指针相遇;如果无环,跳出循环结束
lc.142. 环形链表 II
原题: 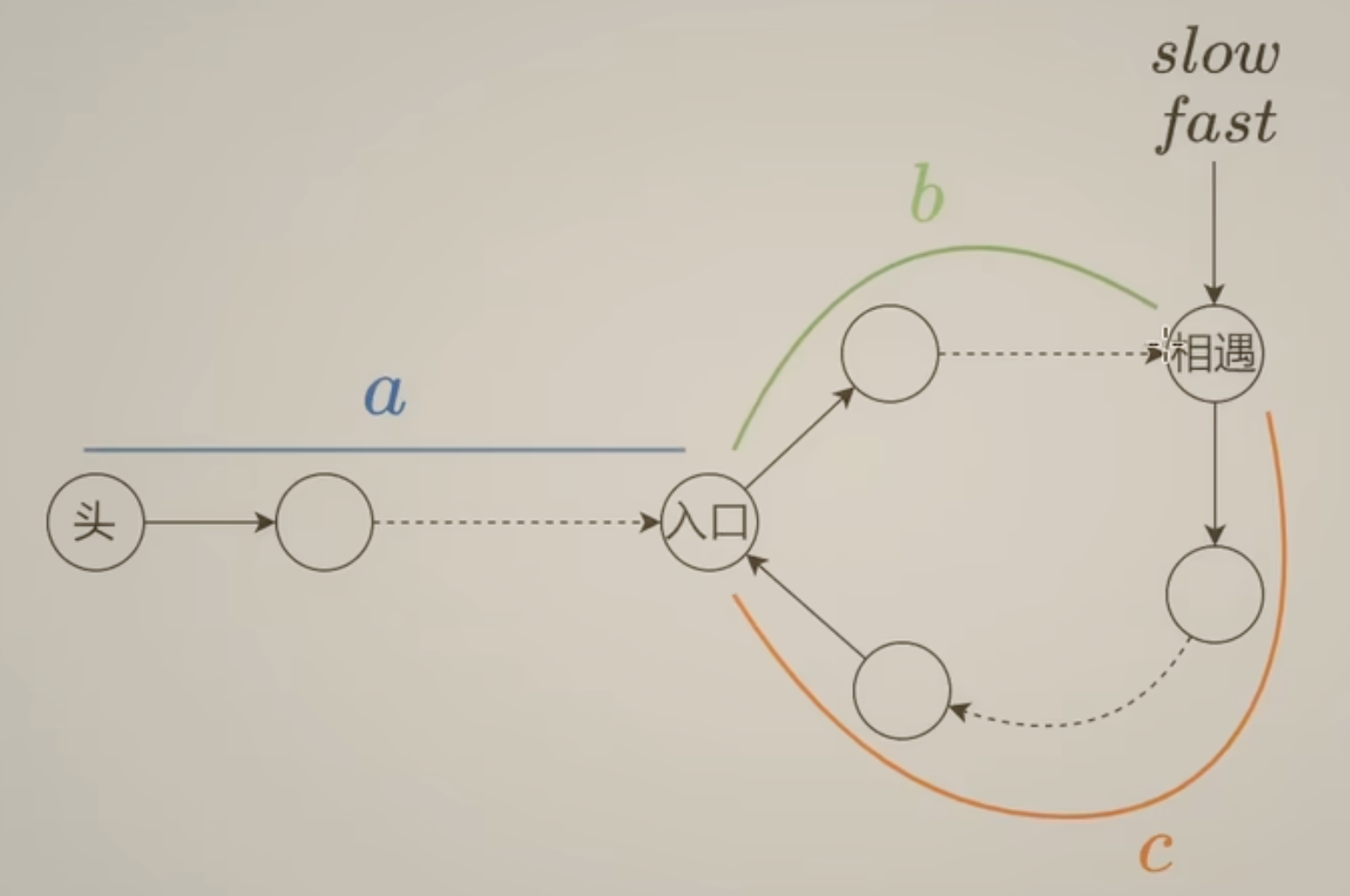
let slow = head;
let fast = head;
while (fast && fast.next) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (fast === slow) {
while (slow !== head) {
slow = slow.next;
head = head.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
return null;解释: 环长 = b + c 慢指针移动的距离 = a + b 快指针移动的距离 = a + b + k(b+c) 快指针移动距离是慢指针的两倍 推导出 2(a+b) = a + b + k(b+c) a-c = (k-1) (b+c)
这意味着 slow 从相遇点开始和 head 节点继续走,最终会相遇。 解释如下:head 走 c 步,slow 也 c 步到了入口,head 再走(k-1)(b+c) 也就是环长到达 a,这时候 slow 也套了 k-1 圈。它们在入口相遇
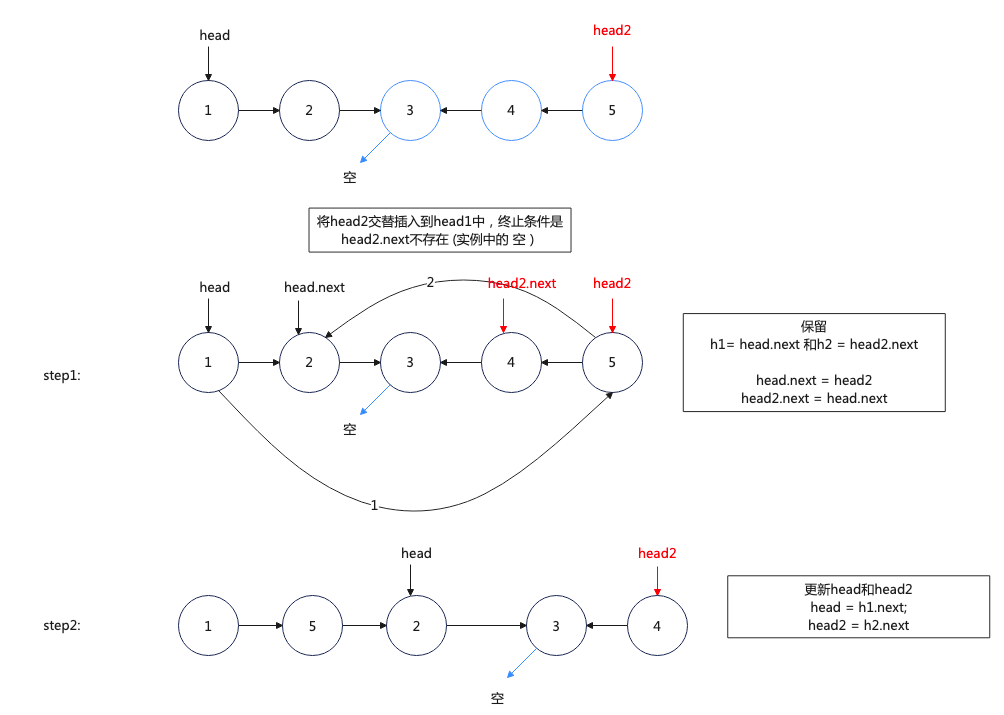
lc.143. 重排链表
原题: https://leetcode.cn/problems/reorder-list/
步骤: 找到中心点, 翻转后半部分链表, 循环交替插入 后半部分链表, 最终得到 L0 -> Ln -> L1 -> Ln-1 -> L2 -> Ln-2
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {void} Do not return anything, modify head in-place instead.
*/
var reorderList = function (head) {
let mid = middleNode(head);
let head2 = reverseList(mid);
while (head2.next) {
let h1 = head.next;
let h2 = head2.next;
head.next = head2;
head2.next = h1;
head = h1;
head2 = h2;
}
};
var middleNode = function (head) {
let slow = head;
let fast = head;
while (fast && fast.next) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
};
var reverseList = function (head) {
let pre = null;
let cur = head;
while (cur) {
let nxt = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = nxt;
}
return pre;
};
删除链表
lc.237. 删除链表中的节点
https://leetcode.cn/problems/delete-node-in-a-linked-list/description/
/**
* @param {ListNode} node
* @return {void} Do not return anything, modify node in-place instead.
*/
var deleteNode = function (node) {
let nodeNext = node.next;
node.val = nodeNext.val;
node.next = nodeNext.next;
};解释:题目含义为只要值不一致,就认为这个节点删除了。而真正意义的删除是这个节点的内存不在这条链上。 所以这里取巧的是直接改掉原来的值。
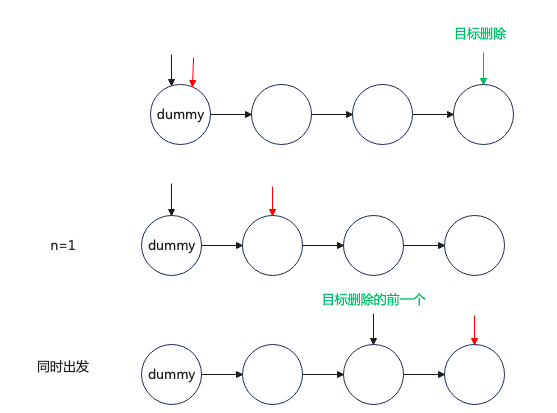
lc.19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-nth-node-from-end-of-list/description/
var removeNthFromEnd = function (head, n) {
let dummyNode = new ListNode(); // 如果可能操作到头节点就需要一个dummy指向head,便于返回
dummyNode.next = head;
let cur = dummyNode;
let right = cur;
Array(n)
.fill(0)
.forEach(() => {
right = right.next;
});
let left = cur; // 找到带删除的上一个节点
while (right.next) {
right = right.next;
left = left.next;
}
left.next = left.next.next;
return dummyNode.next;
};解释:这里使用快慢指针,right 先走 n 步,在和 left 同时出发,left 从 dummy 出发,right 走到最后一个节点,这时候,left 到位置就是被删除节点的上一节点
lc.83. 删除排序链表中的重复元素
https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-list/
var deleteDuplicates = function (head) {
if (!head) {
return head;
}
let cur = head;
while (cur.next) {
if (cur.next.val === cur.val) {
cur.next = cur.next.next;
} else {
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return head;
};lc.82. 删除排序链表中的重复元素 II
与 83 的区别是有重复的,都不要
var deleteDuplicates = function (head) {
let dummy = new ListNode();
dummy.next = head;
let cur = dummy;
while (cur.next && cur.next.next) {
let val = cur.next.val;
if (val === cur.next.next.val) {
while (cur.next && cur.next.val === val) {
// 第一次是自己和自己对比;下一次是和第一次对比
cur.next = cur.next.next;
}
} else {
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return dummy.next;
};解释; 初始化 cur 指向 dummy Node,每次循环的时候 看下一个节点和 下下一个节点 如果一样,就再套一个循环,不断删除节点。知道没有节点或者遇到的节点值不一样。 如果不一样,cur 移到下一个节点,直至满足不足 2 个节点。